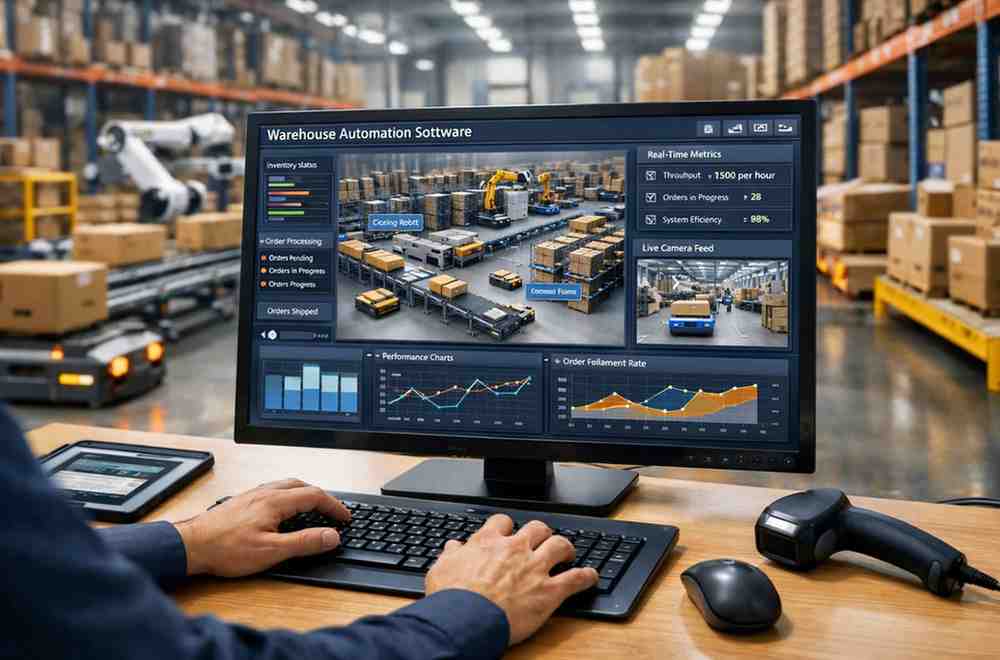
Warehouse Automation Software: Transforming Modern Supply Chains In today’s fast-moving supply chain environment, warehouses are no longer just storage spaces. They are high-performance hubs that directly impact delivery speed, customer satisfaction, and operating costs. As order volumes grow and customer expectations rise, manual processes struggle to keep up. This is where Warehouse Automation Software plays a critical role, helping businesses streamline operations, reduce errors, and scale efficiently. Understanding Warehouse Automation Software Warehouse Automation Software refers to digital systems designed to control, manage, and optimize warehouse operations through automation. These platforms integrate with hardware such as conveyors, robotic picking systems, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), barcode scanners, and IoT sensors. At the same time, they connect with enterprise systems like ERP, WMS, and order management tools. The goal is simple but powerful: replace repetitive, error-prone manual tasks with intelligent, software-driven workflows that improve accuracy, speed, and visibility across the warehouse. Why Warehouses Are Moving Toward Automation Traditional warehouses depend heavily on manual labor for picking, packing, inventory tracking, and dispatch. While this approach works at smaller scales, it becomes inefficient and costly as operations expand. Labor shortages, rising wages, and higher error rates make manual handling less sustainable. Automation software addresses these challenges by coordinating machines and people in real time. It ensures that inventory moves through the warehouse using the most efficient paths, that orders are prioritized correctly, and that stock levels remain accurate. This shift is not just about cutting costs; it is about building resilience and consistency in operations. Core Features That Drive Value A well-designed warehouse automation system offers a range of features that directly impact daily performance: Real-time inventory visibility to reduce stock discrepancies and prevent over- or under-stocking Automated picking and sorting logic to improve order accuracy and throughput Intelligent task allocation that balances workloads between human workers and machines Seamless system integration with ERP, transportation, and order management platforms Data analytics and reporting to identify bottlenecks and support continuous improvement Together, these features create a connected warehouse environment where decisions are based on live data rather than assumptions. Operational Benefits for Businesses The business impact of Warehouse Automation Software is measurable and long-term. One of the most immediate benefits is accuracy. Automated scanning, tracking, and validation drastically reduce picking and shipping errors, leading to fewer returns and higher customer trust. Speed is another key advantage. Automated workflows shorten order fulfillment cycles, enabling faster dispatch and same-day or next-day delivery options. This directly enhances customer satisfaction and brand reputation. Cost efficiency also improves over time. While automation requires upfront investment, businesses often see lower labor costs, reduced waste, and better space utilization. Warehouses can handle higher volumes without proportionally increasing staff or floor space. Scalability and Business Growth As companies grow, warehouse complexity increases. Seasonal spikes, new product lines, and multi-location fulfillment can overwhelm manual systems. Automation software supports scalability by adapting workflows dynamically based on volume and demand. For example, during peak periods, the system can prioritize high-value orders, adjust picking routes, and allocate additional automated resources where needed. This flexibility allows businesses to grow without constant operational restructuring. Industry Use Cases Warehouse automation is no longer limited to large enterprises. E-commerce, retail, manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and logistics providers are increasingly adopting automation software to stay competitive. E-commerce warehouses rely on automation to handle high order volumes with short delivery windows. Manufacturers use it to manage raw materials and finished goods with precision. Pharmaceutical companies depend on automated systems for compliance, traceability, and controlled storage environments. Across industries, the common thread is the need for reliability, visibility, and speed. Implementation Considerations Successful adoption requires more than installing software. Businesses must assess their existing workflows, data quality, and infrastructure readiness. Integration with legacy systems should be planned carefully to avoid disruptions. Employee training is equally important. Automation works best when staff understand how to interact with the system and interpret its insights. A phased rollout often helps organizations adapt smoothly while delivering early value. The Strategic Role of Automation Warehouse automation is not just an operational upgrade; it is a strategic investment. It enables companies to respond quickly to market changes, improve service levels, and maintain control as complexity increases. In an era where fulfillment speed and accuracy define customer loyalty, automation becomes a competitive necessity rather than a luxury. Conclusion In conclusion, Warehouse Automation Software empowers businesses to build faster, smarter, and more resilient warehouse operations. By combining intelligent software with automated systems, organizations can reduce errors, scale with confidence, and deliver consistently high service levels in an increasingly demanding market.